Osm Admin: Object Creation Form
2 years ago ∙ 2 minutes read
Today, I finished implementing an object creation form.
It works according to the specs on Interfaces and Forms. Currently, it only supports string and integer input fields; later, there will be a lot more.
Let's review how it works:
Configuration
All user interface details are configured directly in the data class:
/**
* @property ?int $parent_id #[
* Serialized,
* Table\Int_(unsigned: true, references: 'scopes.id', on_delete: 'cascade'),
* Form\Int_(10, 'Parent Scope'),
* ]
* ...
* @property ?string $title #[
* Serialized,
* Form\String_(20, 'Title'),
* ]
* ...
*/
#[Storage\Scopes, Interface_\Table\Admin('/scopes', 'Scope'), ...]
class Scope extends Object_
{
use Id;
...
}#[Interface_\Table\Admin] attribute creates the user interface for editing scope objects that is accessible at /scopes URL. The second parameter, Scope, is used in various user interface labels and messages. Currently, the user interface handles two routes:
GET /scopes/createroute shows a form page for entering details of a new scope and saving it.POST /scopes/createroute processes form data and creates a record in the underlying database table.
#[Form\*] attributes make parent_id and title properties to appear in the form.
Model
The #[Interface\] and #[Form\*] attributes are reflected into the $osm_app->schema->classes[Scope::class]->interfaces property:
{
"name": "Osm\\Admin\\Scopes\\Scope",
"interfaces": {
"table_admin": {
"type": "table_admin",
"url": "\/scopes",
"form": {
"chapters": {
"": {
"sort_order": 0,
"name": "",
"sections": {
"": {
"sort_order": 0,
"name": "",
"title": "General",
"fieldsets": {
"": {
"sort_order": 0,
"name": "",
"fields": {
"parent_id": {
"type": "int",
"sort_order": 10,
"name": "parent_id",
"title": "Parent Scope",
"template": "forms::field.int"
},
"title": {
"type": "string",
"sort_order": 20,
"name": "title",
"title": "Title",
"template": "forms::field.string"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
...
}
},
...
}Form Rendering
The GET /scopes/create route renders the form using its template. It passes the form definition, mode and initial form data:
/**
* @property \stdClass $data
*/
#[Interface_(Admin::class), Name('GET /create')]
class CreatePage extends Route
{
public function run(): Response {
return view_response($this->form->template, [
'form' => $this->form,
'mode' => Form::CREATE_MODE,
'data' => $this->data,
]);
}
protected function get_data(): \stdClass {
return (object)[];
}
}The form template, forms::form renders its only chapter, the chapter renders the only section, the section renders its only fieldset, and, finally, the fieldset renders the two fields, using forms::field.int and forms::field.string field templates:
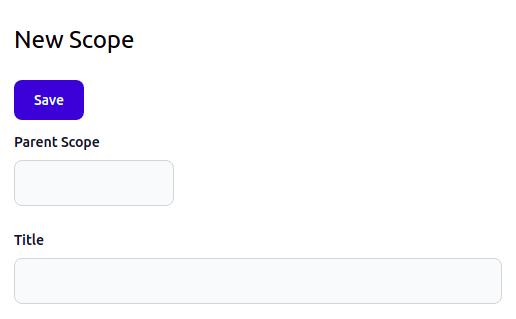
Submitting Form Data
The Save button, or pressing Enter submits the form data to the POST /scopes/create route via AJAX. Here is how it works.
The JavaScript Form controller class is attached to the <form> element using the data-js-form attribute:
<form ... data-js-form="...">
...
</form> This controller prevents default browser data submission behavior. Instead, it collects field data into a JSON manually, and sends it to the server. Once, server confirms that the scope object is created, it redirects to the object editing page using the edit form url received from the server:
...
export default register('form', class Form extends Controller {
get events() {
return Object.assign({}, super.events, {
'submit': 'onSubmit',
});
}
onSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
fetch(this.element.action, {
method: this.element.method,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(this.data),
message: this.options.s_saving_new_object,
})
.then(response => {
notice(this.options.s_new_object_saved);
return response.json();
})
.then(json => {
location.href = json.url;
})
.catch(() => null);
}
...
});Collecting Form Data
The Form controller collects the form data by calling the data() method of every field controller:
...
export default register('form', class Form extends Controller {
...
get data() {
let data = {};
this.fields.forEach(field => field.data(data));
return data;
}
});Field controllers are attached to the field HTML elements using data-js-* attributes. For example, the string field controller is attached using the data-js-string-field attribute:
<div class="field ..." data-js-string-field>
...
</div>The data method of a field controller adds the field data to the provided object:
export default register('string-field', class String_ extends Field {
data(data) {
if (this.value.trim()) {
data[this.name] = this.value.trim();
}
}
get input_element() {
return this.element.querySelector('input');
}
get name() {
return this.input_element.name;
}
get value() {
return this.input_element.value;
}
});The resulting JSON containing the form data is:
{"parent_id":1,"title":"English"}Processing Form Data
The form data is processed by the POST /scopes/create route:
#[Interface_(Admin::class), Name('POST /create')]
class Create extends Route
{
public function run(): Response
{
$item = json_decode($this->http->content, flags: JSON_THROW_ON_ERROR);
if (!is_object($item)) {
return plain_response('Object expected', 500);
}
$id = query($this->class_name)->insert($item);
return json_response((object)[
'url' => $this->interface->url("/edit?id={$id}"),
]);
}
}
